Insulin Pump Therapy
What is an insulin pump?
An insulin pump is a small, battery-operated device (about the size of a pager) that can replace insulin injections for patients managing diabetes. The purpose of a pump is to provide an accurate, continuous controlled delivery of insulin, in pulses which can be regulated by the user to meet their Glucose control objectives.
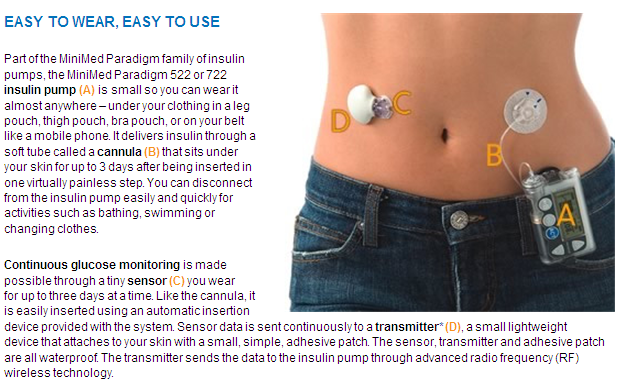
How does an insulin pump work?
The pump delivers insulin from a reservoir inside the pump, through a thin plastic tube (called an infusion set), to the body. Most infusion sets are worn in the abdominal area and use a tiny, flexible tube, called a cannula, which is inserted easily into the skin using an insertion device. Patients generally refill their insulin and change their infusion sets every two to three days.
A pump is easy to program and automatically delivers a constant rate of insulin - called a "basal rate"- to keep blood glucose in the desired range between meals and over night. Guided by a physician, the user creates a customized basal pattern, with the goal of closely matching individual needs. Pump users can easily adjust the pump for changes in lifestyle needs, and can program insulin delivery at mealtimes.
- Pump therapy is simple . It is based on what your body does naturally - deliver small pulses of insulin all the time and little extras controlled by the patient at mealtimes to cover the food intake.
- The pump helps achieve "tight glucose control ." Diabetes patients can easily adjust insulin to keep glucose levels within a near-normal range. A pump can help patients avoid hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar), which can degrade health over time, and hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), an acute condition that can be very dangerous, particularly at night while a patient sleeps.
- The pump more closely mimics a healthy pancreas . An insulin pump more closely mimics a healthy pancreas by delivering insulin effectively, continuously and with minimal variability. A healthy pancreas delivers insulin every 10 to 14 minutes. A pump more closely mimics the pancreas by continually delivering insulin around the clock and allowing patients to program multiple basal rates depending on their individual needs.
- The pump is precise and accurate . Insulin pumps can deliver insulin precisely and accurately in 0.1 unit increments, which is nearly impossible for people using traditional injection therapy.
- With the pump, people can be more flexible . Unlike patients using longer-acting insulin with injection therapy who must follow rigid schedules of insulin injections, meals and snacks, patients using an insulin pump can program insulin delivery when they eat, and adjust or stop insulin delivery for exercise or other needs. Patients using pump therapy can eat what they want, when they want -- something almost unheard of in patients treating their condition with traditional insulin injections.

